Zeroth Law
The zeroth law is a consequence of thermal equilibrium and allows us to conclude that temperature is a well-defined physical quantity. The zeroth law of thermodynamics states:
If a body A and a body B are both in equilibrium with each other; then a body C which is in thermal equilibrium with body B will also be in equilibrium with body Aand the temperature of body C is equal to the temperature of body A.
It is the zeroth law, because it preceeds the first and second laws of thermodynamics and is also a tacit assumption in both laws.
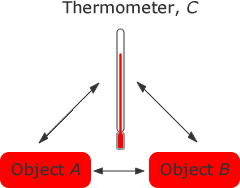
We use the zeroth law when we wish to compare the temperatures of two objects, A and B. We can do this by using a thermometer, C and placing it again object A it reaches thermal equilibrium with object A and measure the temperature of A. Placing the thermometer against object B until thermal equilibrium is reached we measure the temperature of object B. If they are the same temperature then they will be in thermal equilibrium with each other.